
Zero-Drift - Op amps that are characterized by low offset voltages and low offset drift with temperature. This should be included in any general op amp search. Voltage Feedback - Unless specified as a current feedback amplifier, all op amps use voltage feedback. Variable Gain - Similar to a programmable gain amp, but the gain may be controlled digitally or with an analog voltage. Transimpedance - An amplifier that takes a current input and produces a voltage output. Transconductance - An amplifier that takes a voltage input and produces a current output. Sample and Hold - Typically used with ADCs, these amplifiers will hold an output value long enough for a conversion to complete. #Op amp offset decreasing voltage serial
This can be done with selection pins or through a serial interface like SPI.
Programmable Gain - Op amps with variable gain that can be programmed digitally. Power - An op amp with an output power stage allowing it to source more current than a typical op amp. Logarithmic - Amplifiers with an output that is proportional to the log of the input relative to a reference. Limiting - Amplifiers that can internally clamp the output voltage. These have higher input impedances and lower input bias currents than bipolar devices. JFET - Op amps made with JFET processes. Isolation - Op amps with a built in optoisolator to physically isolate the input from the output. These amps are designed for high precision, high input impedance, and high open-loop gain. Typically inputs pass through buffer amplifiers and then are fed into a differential amplifier. Instrumentation - These amplifiers are most often composed of 3 separate amps. A differential is designed to amplify the difference between two signals. Differential - All op amps are technically differential amplifiers, but are often used to amplify a single signal. Current Sense - An op amp used to measure a small voltage drop across a resistor where the output voltage is proportional to the current through the resistor. These op amps typically have a faster slew rate and frequency-independent gain. Current Feedback - An op amp with an output that is proportional to current rather than voltage. CMOS op amps typically have higher input impedance and lower power consumption than bipolar devices. CMOS - CMOS process technology is used in the op amp rather than a traditional bipolar process. These typically only have one input and cannot be used as a normal op amp. Buffer - The op amp is pre-configured to be used as an analog buffer, normally with unity gain. The amps in this category do not have an output power stage. 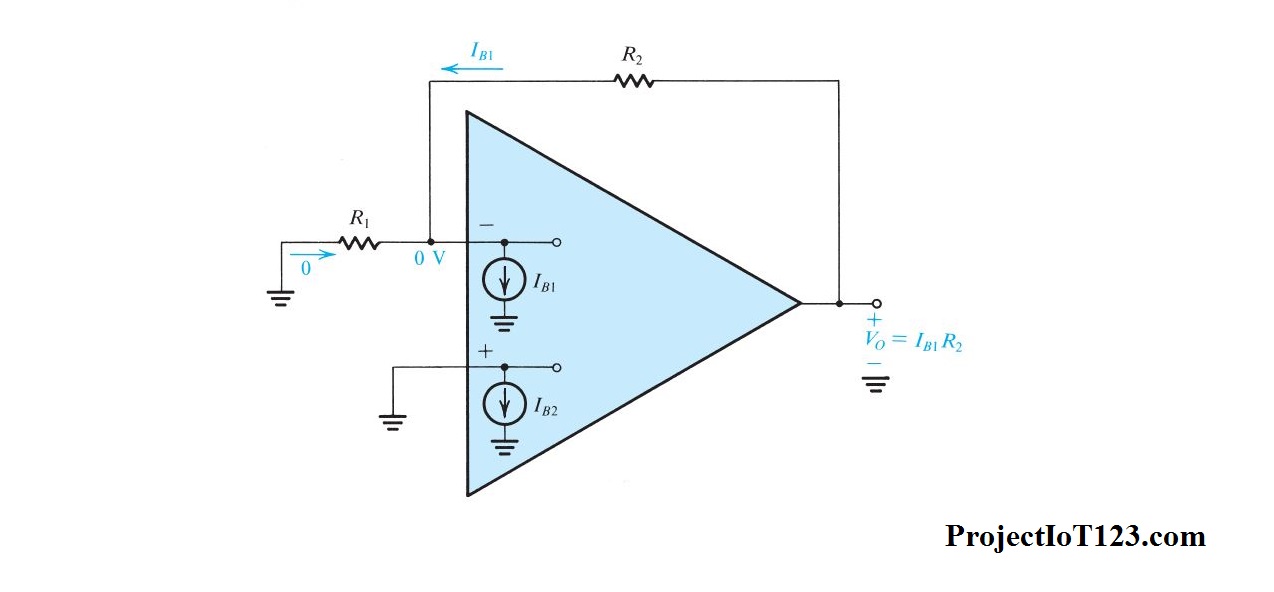 Audio - These op amps are optimized for low noise and distortion for audio.
Audio - These op amps are optimized for low noise and distortion for audio.  Most op amps fall under the General Purpose category, however there are many other categories that some op amps may fall into.
Most op amps fall under the General Purpose category, however there are many other categories that some op amps may fall into. 
The following list breaks down the parameters used by the Digi-Key filters for the op amp family. Like many ICs, op amps have a wide variety of specifications to keep in mind. Keep these parameters in mind when looking through the realistic parameters below.
Zero input offset voltage - the op amp’s output is zero when its inputs are equal. Zero input bias current - no current flows into the input terminals. Infinite slew rate - the op amp’s output can change as fast as it needs to. Infinite bandwidth - the op amp’s gain is not affected by frequency. Some of the characteristics of an ideal op amp are: The ideal model exists to make the math involved in design easier, but cannot exist in practice. Image source: Wikimedia Commons / CC-BY-SA-3.0 / GFDL The Ideal Modelīefore looking at the specifications of a real op amp, it is important to understand the ideal op amp model to establish a reference.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
